LOCOMOTION
Locomotion: The movement of an individual from one place to another is called locomotion. It occur in both unicellular and multicellular organism with the help of different structure.
For example, hydra uses tentacles for capturing its prey/food as well as for locomotion. Paramoceium uses cilia for movement of food (ingestion) and locomotion . Human uses limbs for changes in body postures and locomotion.
FUNCTION OF LOCOMOTION
(I)Searching and building of shelter.
(II)Finding mate.
(III) Protection from Predator.
(IV)Search of suitable breeding grounds.
(V)Migration.
(II)Finding mate.
(III) Protection from Predator.
(IV)Search of suitable breeding grounds.
(V)Migration.
MOVEMENT
Movement is a change in a posture or position. It is an essential and significant features of living organism and hence both unicellular and multicellular organism show movement. For example, unicellular organisms such as a Amoeba move with the help of pseudopodia, streaming of protoplasm in amobia is a simple form of Movement. In many other organism, different structures cilia, flagella, limbs,jaws,eyelids, tongue etc. show movement.
MOVEMENTS OF EXTERNAL BODY PARTS
(I) To maintain equilibrium of the body-limbs, head,trunk etc. play an important role.
(II) The movement of limbs, appendages,jaws , tentacles, tongue in organisms help to capture food.
(III) Movement of limbs is responsible for ingestion , defence, locomotion.
MOVEMENT OF INTERNAL BODY PARTS
(I)The food from the mouth moves to the stomach for digestion through the peristaltic movement of the oesophagus.
(II)Pumping of heart for circulating blood to different part of the body.
(II)Pumping of heart for circulating blood to different part of the body.
TYPES OF MOVEMENT
(I) Amoeboid or Pseudopodial movement: Due to the streaming of protoplasm and cytoplasm, the surface of the cell form false feet or pseudopodia. The old pseudopodia are replaced by a new psedopodia and therefore the formation and withdrawal of its allows the cell to change its shape regularly. As Amoeba, WBC, and macrophages show pseudopodial movement they do not have a fixed shape. The leukocyte and macrophages reach each and every part of the body and engulf the antigen or pathogen through this psedopodia.
(II) Ciliary movement: The free surface of the cells have a short fine hair like a projection called Cilia. The movement of these projection (cilia) is called ciliary movement.
(III) Mascular movement: In humans, movement of limbs, jaw , tongue and other body parts occurred due to contraction of muscles.
ALL LOCOMOTIONS ARE MOVEMENTS BUT ALL MOVEMENTS ARE NOT LOCOMOTIONS.
MUSCLES
Muscle is a specialised tissue or generated from the germ layer, mesoderm. The muscular tissue is made up of specialised cells called myocytes. These cells are bounded together by a connective tissue and form muscular tissue. It brings about different type of Movement in internal and external body parts.
TYPES OF MUSCLE
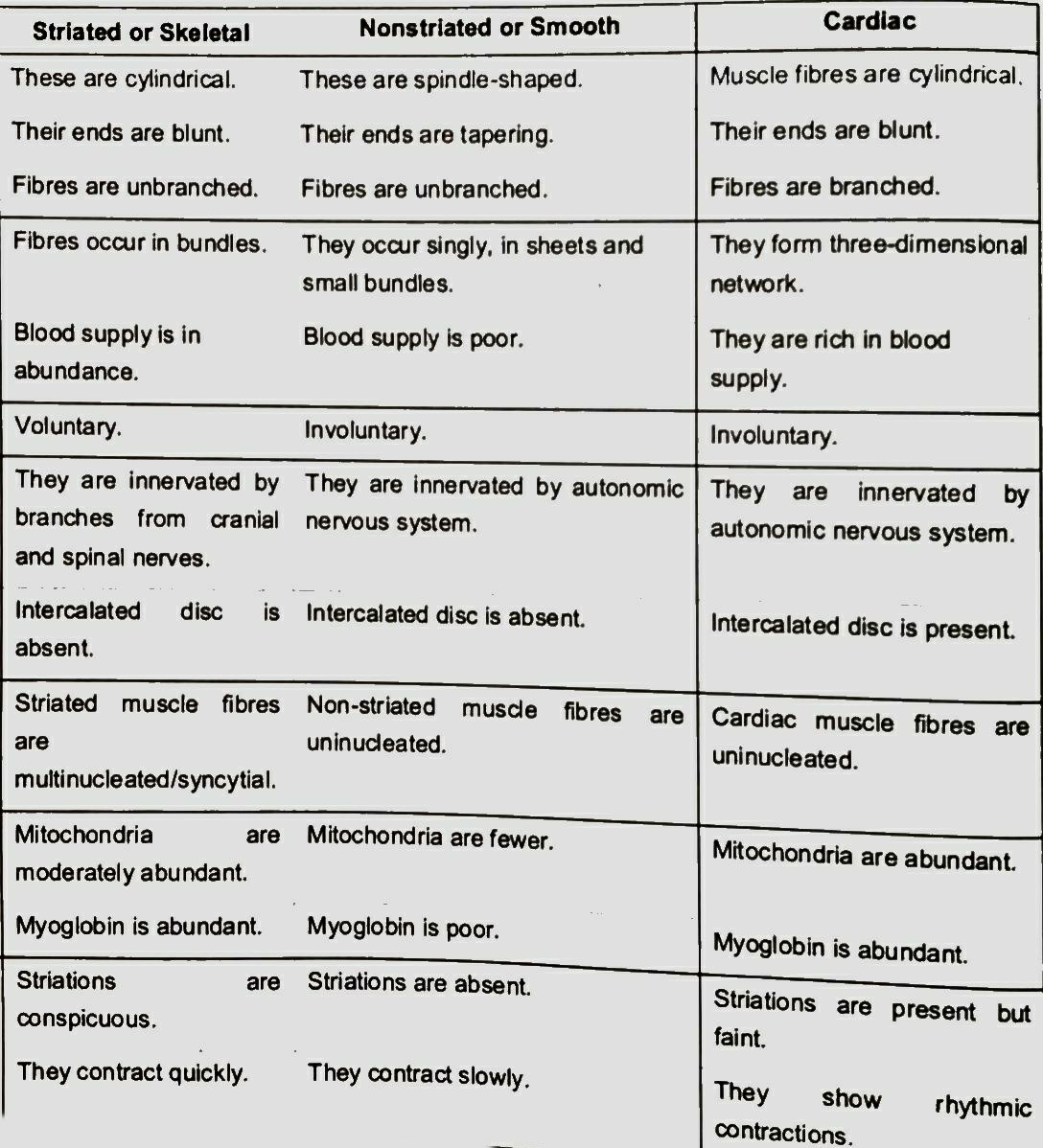
(I) Skeletal muscle or striped or voluntary muscle or striated: These muscles are attached to the skeleton component of the body and a primary involved in locomotory actions and change of body posture.these muscles are voluntary as they are under the control of animals will or conscious. For example, muscle of hindlimbs, forelimbs, body walls, tongue, pharynx and beginning of oesophagus etc.
(II) Smooth or non-striated or non-striped or involuntary muscles: The cells of these muscles are elongated, spindle shaped, broad from the middle and have tapering ends. 20 muscles lines the hollow organs and involuntary. e.g., posterior region of oesophagus, stomach, intestine, lungs, urinary bladder, urinogenital tract.
(III) Cardiac muscles: Cardiac mean heart, hence muscle of the heart are called cardiac muscles.
Facts:
(I) Kangaroos cannot walk backwards.
(II) A human body is made up of 639 muscles.
(III) It takes 17 muscles to smile.
(IV) There are muscles in the root of our hair that give us goosebumps.
(V) The busiest muscles in the body are muscles of eyes.
POINTS:
1.Both internal and external structure of an organism show movement.
2.locomotion occur in both unicellular and multi cellular organism.
3. Movement and locomotion are interdependent on each other.
4. Cells of human exhibit three kinds of movement ciliary, Pseudopodial and muscular.
5. The movement which occurs through pseudo podia is called Pseudopodial movement. It is shown by WBC and macrophages.
6. The movement which occur due to cilia are called ciliary movement. It occur in digestive tract, fallopian tube etc.
7.Movement of limbs, jaws, tongue occur due to contraction and relaxation of muscles.
8. Muscle is a specialised tissue originated from mesoderm.
9.Nerve impulse, hormones, mechanically, thermal or chemical stimulus are required for excitation of the muscles.
********************




0 Comments